|
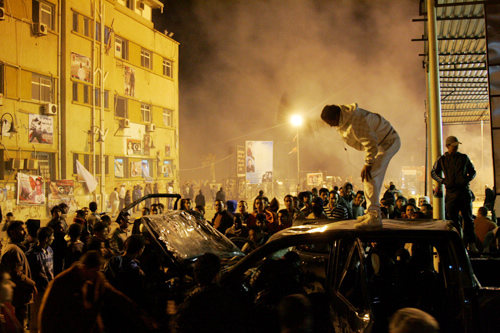 |
|
UNITY OR SEPARATION?: Opponents of federalism damage a vehicle belonging to pro-federalism protesters in the eastern city of Benghazi on March 16 (XINHUA/AFP) |

On March 19, 2011, France launched the first air assault on Libya, starting the half-year-long armed intervention led by NATO in the North African country. With the strong support of the West, the rebels eventually toppled Muammar Gaddafi, who had ruled Libya for over 40 years.
The war caused more than 20,000 casualties in a country with a population of only 6 million and made 700,000 Libyans refugees. Although it led to the fall of the embattled Gaddafi regime, the war has not brought expected positive changes to Libya. As its negative aftermath continues to take a toll on the country, prospects for a prosperous, stable and united Libya remain dim.
Religious extremist forces that were suppressed for a long time again became active in Libya after the collapse of the Gaddafi regime. Facing the increasing expansion of religious forces, the National Transitional Council (NTC), Libya's new government, said the new Constitution should be drafted on the basis of Islamic classics. It even suggested reinstating the polygamy system that was abolished by Gaddafi, arousing the opposition of many Libyans and the discontent of the West. Western countries complained that they had helped a conservative religious regime, to which the West is strongly opposed.
Under these circumstances, the NTC claimed that the emerging religious groups are moderates, and religious extremists are not widely representative in Libya. The NTC had to play the role of a coordinator between religious groups at home and the West to satisfy the demands of the religious groups and ease the anger of Western allies.
Religion's influence on politics has been enormously weakened in the modern era. Theocratic rule has become increasingly unpopular. Recent developments in postwar Libya that run counter to this trend have posed serious challenges to the new government. The NTC faces the daunting task of leading Libyan reconstruction, including drafting a modern Constitution and establishing a political system that separates religion from politics.
Similarly, Islamist political parties achieved success in elections in Egypt and Tunisia after their former regimes were overthrown. Yemen's religious extremists even announced they would found their own Islamic emirate. The West had not expected religious forces would rapidly emerge following the turmoil in the Middle East. This is the last thing that it wants to see in the region.
Since the fall of the Gaddafi regime, Libya has fallen into divided status. Cyrenaica in east Libya announced on March 6 it would seek autonomy. While nominally obeying the order of the NTC in diplomatic and defense affairs, it vowed to establish its own armed forces.
Misrata, the third largest city in Libya, also prepared to establish self-government. The Misrata Government elected in February has taken many measures to control the population flows of the region.
The NTC strongly opposes all forms of self-government in Libya. At the same time, residents in Tripoli and Benghazi took to the streets to protest separation. They know clearly that demands for autonomy would lead to the split of the country or even a civil war. If the NTC fails to control the country and build a stable central government, the break-up of Libya seems inevitable.
| 