|
 |
|
MILESTONE MEETING: IMF and World Bank members at a joint meeting on April 25 in Washington, D.C. (ZHU WEI) | At the G20 Pittsburgh Summit in September 2009, members agreed to a 5-percent IMF quota share transfer to developing counties. But so far the quota realignment process is far from finish.
Zhou said the quota adjustment and reform is not a zero-sum game. "The IMF with a more reasonable governance structure will be better able to protect global economic and financial stability which will benefit all member countries," Zhou said.
China currently ranks sixth with a 3.72-percent quota share in the IMF. The United States has a 17.4-percent share. Developed countries as a whole control a majority 57 percent.
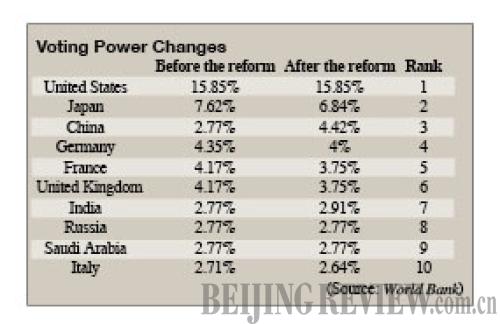
Main Components of the WB's Reform Package
1. Financial Resources:
- an increase of $86.2 billion in capital for the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), and
- a $200-million increase in the capital of the International Finance Corp. (IFC), the World Bank Group's private sector arm.
2. Voting Power:
- a 3.13-percentage point increase in the voting power of Developing and Transition countries (DTCs) at the IBRD, bringing the total to 47.19 percent;
- the IBRD 2010 realignment that will result from a selective capital increase of $27.8 billion;
- an increase in the voting power of DTCs at IFC to 39.48 percent;
- the IFC 2010 realignment that will result from a selective capital increase of $200 million and increase in the basic votes for all members; and
- an agreement to review IBRD and IFC shareholdings every five years with a commitment to equitable voting power between developed countries and DTCs over time.
3. Post-Crisis Strategy:
- targeting the poor and vulnerable, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa;
- creating opportunities for growth with a special focus on agriculture and infrastructure;
- promoting global collective action on issues from climate change and trade to agriculture, food security, energy, water and health;
- strengthening governance and anti-corruption efforts; and
- preparing for crises.
4. Operational Reforms:
- a new Access to Information Policy that makes the bank a world leader among multilateral institutions on information disclosure.
- the bank's Open Data Initiative that puts it at the forefront of giving free and easy access to information on developing countries;
- investment lending reform; and
- strengthened governance and anti-corruption efforts.
(Source: World Bank)
1. Financial Resources:
- an increase of $86.2 billion in capital for the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), and
l a $200-million increase in the capital of the International Finance Corp. (IFC), the World Bank Group's private sector arm.
2. Voting Power:
- a 3.13-percentage point increase in the voting power of Developing and Transition countries (DTCs) at the IBRD, bringing the total to 47.19 percent;
- the IBRD 2010 realignment that will result from a selective capital increase of $27.8 billion;
- an increase in the voting power of DTCs at IFC to 39.48 percent;
- the IFC 2010 realignment that will result from a selective capital increase of $200 million and increase in the basic votes for all members; and
- an agreement to review IBRD and IFC shareholdings every five years with a commitment to equitable voting power between developed countries and DTCs over time.
3. Post-Crisis Strategy:
- targeting the poor and vulnerable, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa;
- creating opportunities for growth with a special focus on agriculture and infrastructure;
- promoting global collective action on issues from climate change and trade to agriculture, food security, energy, water and health;
- strengthening governance and anti-corruption efforts; and
- preparing for crises.
4. Operational Reforms:
- a new Access to Information Policy that makes the bank a world leader among multilateral institutions on information disclosure.
- the bank's Open Data Initiative that puts it at the forefront of giving free and easy access to information on developing countries;
- investment lending reform; and
- strengthened governance and anti-corruption efforts.
(Source: World Bank)
| 